low cycle fatigue at high temperature with creep rocket throat|Stress analysis & life prediction of a cryogenic rocket engine : solutions The inner and outer walls are bonded together by brazing at high temperature. Failure of a double walled chamber occurs due to thinning of the inner wall and bulging into the chamber . Resultado da 3 dias atrás · 1.000 episódios. O Astrólogo mais querido do Brasil traz as novidades para cada signo! Descubra as previsões dos astros nos .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webApós uma tragédia, que forçou o jovem Príncipe TChalla a assumir o trono de Wakanda, ele é confrontado em um teste final, pondo em risco o destino de seu país e do mundo inteiro. Em conflito contra sua própria família, o novo rei deve reunir seus aliados e liberar o poder total da Pantera Negra para derrotar seus inimigos e abraçar o seu futuro como um .
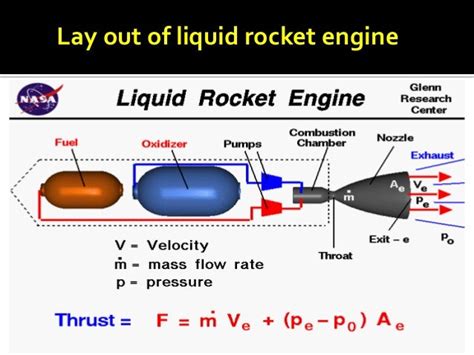
Rocket engine thrust chambers withstand very high temperatures and thermal gradients during service that induce multiple damaging phenomena such as plasticity, low .The inner and outer walls are bonded together by brazing at high temperature. Failure of a double walled chamber occurs due to thinning of the inner wall and bulging into the chamber .Due to the lack of test data, bond properties are assumed to take on the weaker material properties. The EBF3 material penetrates the substrate. A copper Inconel alloy layer is .
The numerical simulation of rocket engine thrust chambers is very challenging as several damaging phenomena, such as plasticity, low-cycle-fatigue (LCF) and creep occur .
Thermostructural Numerical Analysis of the Thrust Chamber of a
Structural failure of the chamber occurs due to repeated hot tests of the engine by low cycle fatigue (LCF), high temper-ature creep and thermal ratcheting of inner wall. In this paper, . The failure mode of stainless steel and copper alloys are creep and low cycle fatigue (LCF). The research also explored the different alloy plasticity models and details of cyclic stress analysis carried out for the double-walled . Structural failure of the chamber occurs due to repeated hot tests of the engine by low cycle fatigue (LCF), high temperature creep and thermal ratcheting of inner wall. In this .The failure mode of stainless steel and copper alloys are creep and low cycle fatigue (LCF). The research also explored the different alloy plasticity models and details of cyclic stress analysis .
Modes of failure of the inner wall studied are due to low cycle fatigue failure, creep rupture, thermal ratchetting. The probabilistic fatigue/creep coupling optimization of turbine bladed disks was implemented by regarding the rotor speed, temperature, and density as optimization parameters; the creep stress .
2.3 High Temperature LCF Properties of Copper Alloy [4] Low cycle fatigue life of this material evaluated at 873 K for different plastic strain ranges has been fit into a Coffin– Manson type model as given below: N f ¼ 45:76 De 1 0:6267 ð1Þ where N f = number of cycles to failure, De = cyclic strain range in %. 2.4 High Temperature Creep . Rocket engine thrust chambers withstand very high temperatures and thermal gradients during service that induce multiple damaging phenomena such as plasticity, low-cycle-fatigue (LCF) and creep. .
Keywords: Creep, cyclic stress-stra in, high temperature, low cycle fatigue,Chaboche mode l, ratchetting. I. Introduction Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines (LPRE) ar e commonly used in space . Liquid rocket engine suffers high temperature and pressure difference which is the reason for failure and life limitation, . The failure mode of stainless steel and copper alloys are creep and low cycle fatigue (LCF). . the temperature difference between the inner wall at the throat section is 135.41 K (243.73 °F). For different inner wall .
The detrimental influence of temperature and creep deformation damage on the structural performance of such components has for several decades posed a serious challenge to the work of scientists and engineers, and the methods developed to account for creep fatigue interaction require extensive testing and work for being calibrated and . Extended constant life diagrams for low cycle fatigue and creep-fatigue assessments of high-temperature structures. Author links open overlay panel Zhiyuan Ma a, Zhuojia Fu a b, Haofeng Chen c d, . High-temperature low cycle fatigue, creep–fatigue and thermomechanical fatigue of steels and their welds. Int J Mech Sci, 48 (2006), pp. 160-175.a resultant of the substantial temperature gradient between the hot gas and the low temperature of the coolant, along . is applicable for LCF, but not for high cycle fatigue (HCF). A time dependent model for RLV incorporates specific mission profiles: acceptance test (3-4 cycles 215- 890s), . creep, fatigue (with crack initiation and .
The nickel-based superalloy Inconel 718 is frequently used for various high-temperature components due to its exceptional resistance to oxidation and creep [1], [2].These components typically operate at temperatures below 650 ∘ C. However, in the case of a rocket engine or a gas turbine disc in a modern jet engine, the operating temperature may exceed .
the life caused by fatigue, creep, and thinning after each firing cycle. In order to analyze the life of the thrust chamber, a LOX/Kerosene rocket engine is investigated in this paper. The life . Structural failure of the chamber occurs due to repeated hot tests of the engine by low cycle fatigue (LCF), high temperature creep and thermal ratcheting of inner wall. In this paper, cyclic stress analysis of the thrust chamber is done using ANSYS (Version 16) code. The inner liner of a combustion chamber of a cryogenic liquid rocket engine is exposed to a high load induced by the high temperature of the hot gas and the low temperature of the coolant.
The low-cycle fatigue test and the compression creep-fatigue test of the cast Al-9Si-CuMg alloy for cylinder heads were carried out at high temperature. The cyclic mechanical response characteristics of the material under two kinds of test loads were analyzed. The microstructural evolution process and fracture mechanism of the material in the process of . In general, such thermal fatigue has been examined by low-cycle fatigue experiments under constant temperature, into which a strain-holding process is introduced [7].Creep–fatigue life on the basis of stress-holding-type creep–fatigue data had been assessed [5].Later, the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) constructed a material database . Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) application of the very high temperature nuclear reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950 °C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue behavior. Initial .Fatigue failures occurring at relatively high stress and low number of cycles (of the order < 10 4 ) are termed as low cycle fatigue failures. Low Cycle Fatigue (LCF) is an important consideration in the design and operation of high .
Fatigue at high temperature is a complex phenomenon as it is influenced by a number of time-dependent processes which become important at elevated temperatures. These processes include creep, oxidation, phase instabilities and dynamic strain ageing (DSA), acting either independently or synergistically influence fatigue behaviour, often lowering the fatigue life. .
Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) application of the Very High Temperature Nuclear Reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950 degrees C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue behavior. Initial .

Creep–fatigue interaction occurs in many structural components of high-temperature systems operating under cyclic and steady-state service conditions, such as in nuclear power plants, aerospace . The creep and low cycle fatigue behaviour of a nickel-base superalloy was investigated. The creep curves show an obvious primary creep stage followed by a short steady-state creep stage and then an accelerating creep stage leading to failure at 700. °C.. The 900 °C creep curves demonstrate a shorter primary stage, and a longer accelerating creep stage . Over the decades, the constant life diagram has become an important tool for engineering design and assessment. For specific materials, the effect of mean stress and stress amplitude on the fatigue life is considered in traditional constant life diagrams. In this study, the concept of the structural constant creep-fatigue life diagram is proposed for engineering .
windows 10 memory hard drive test
windows 10 please run hard disk test
Rocket engine thrust chambers withstand very high temperatures and thermal gradients during service that induce multiple damaging phenomena such as plasticity, low-cycle-fatigue (LCF) and creep. . Expand After some cycles, the “doghouse” shape failure of cooling channels characterized by the thinning and bulging of the inner wall would occur. 9 The potential failure modes are creep rupture, low-cycle thermal fatigue and thermal-mechanical ratcheting. 8 The thermal-structural analysis of the thrust chamber wall is significant for the design .
A comparative study on the low-cycle fatigue properties of 316LN austenitic stainless steel with and without a hold period at the maximum tensile strain was performed. Different hold periods (0 s, 60 s, 120 s, 300 s, 1800 s) at a constant strain amplitude of ±0.8% were employed in creep-fatigue tests at 550 °C. Dynamic strain aging (DSA), creep and .
High temperature low cycle fatigue P RODRIGUEZ and S L MANNAN Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research, Kalpakkam 603 102, India Abstract. Fatigue at high temperature is a complex phenomenon as it is influenced by a number of time-dependent processes which become import- ant at elevated temperatures. The creep-fatigue interaction (CFI) tests of a TiAl alloy were carried out at 750 °C and 800 °C in air to investigate the effect of dwell time on fatigue life. The low cycle fatigue (LCF) and creep tests were also conducted for comparison. The life to failure decreased with increasing dwell time and decreased with increasing minimum strain rate.
Keywords: Creep, cyclic stress-strain, high temperature, low cycle fatigue,Chaboche model, ratchetting. I. Introduction Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines (LPRE) are commonly used in space technology.
Stress analysis & life prediction of a cryogenic rocket engine
Numerical Investigation on the Service Life of a Liquid Rocket
Resultado da Acompanhantes trans e travestis na Região Centro de Atibaia - SP | Fatal Model. Selo de Influência Fatal Model. Este anúncio pertence a uma .
low cycle fatigue at high temperature with creep rocket throat|Stress analysis & life prediction of a cryogenic rocket engine